Arrays and Hashtables
Very often we have to handle collections in scripts. The most used collection in Powershell is array.
Arrays
An array is a data structure that is designed to store a collection of items. The items can be the same type or different types. A type can be string, integer, object etc.
Define array
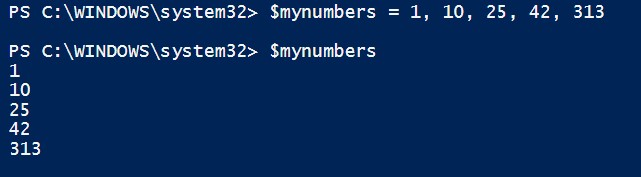
There are many way to define an array The easist way is just seperate elements with commas. Here is an array of numbers:
$mynumbers = 1, 10, 25, 42, 313
$mynumbers
The another way is use the @.
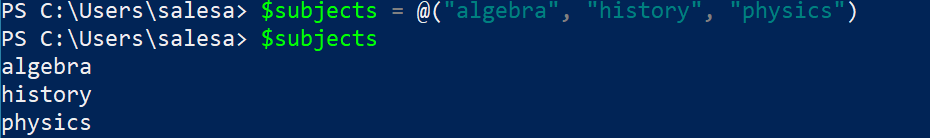
Here is an array of strings:
$subjects = @("algebra", "history", "physics")
$subjects
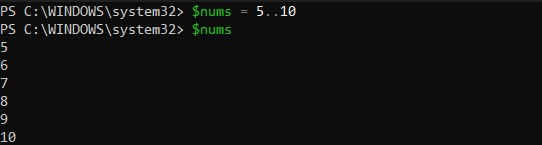
You can also create and initialize an array using the range operator (..)
The following example creates an array containing the values from 5 to 10.
Methods for array
For to manage arrays there are some useful methods for them or we can use some useful commands.
Get element
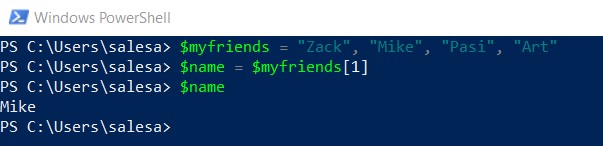
To get an element of the array, use index.
$name = $myfriends[1]
Add element
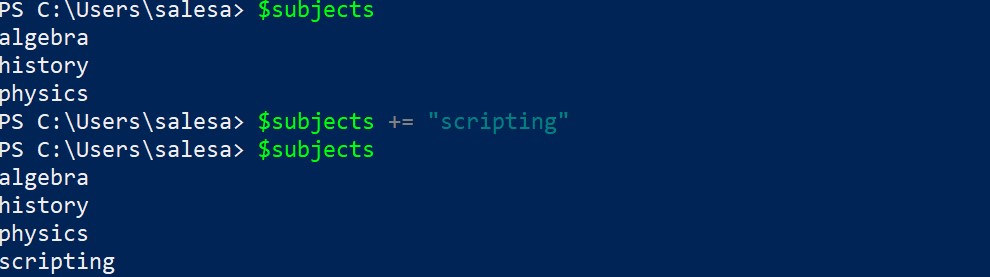
The way to add a new element to an existing array is to use the += operator as shown here.
Sort array
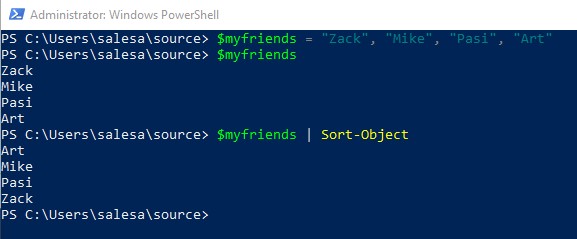
Here is an array of strings, which will be sorted with cmdlet Sort-Object.
$myfriends = "Zack", "Mike", "Pasi", "Art"
Iterations over array elements
You can use looping constructs, such as ForEach, For, and While loops, to refer to the elements in an array. An example, to use a ForEach-loop to display the elements in the $a array:
$a = 0..9
foreach ($element in $a) {
$element
}
More about looping can be read here
Polymorphic Arrays
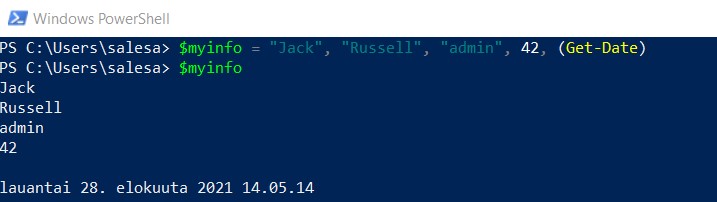
Just like variables, individual elements of an array can store any type of value you assign. This way, you can store whatever you want in an array, even a mixture of different data types. You separate the elements using commas:
$myinfo = "Jack", "Russell", "admin", 42, (Get-Date)
PowerShell Commands Return Arrays
Please, note that PowerShell commands return arrays. It is possible to get the element of array also with a property name.
In the following example, we will get the date property of date object.
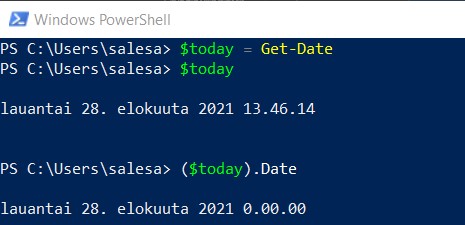
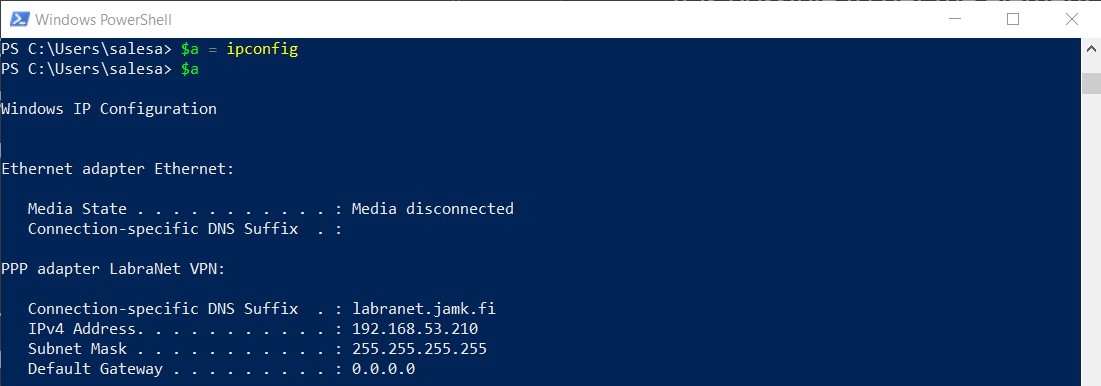
In the following example, we will set ipconfig to variable $a. The variable $a is an array.
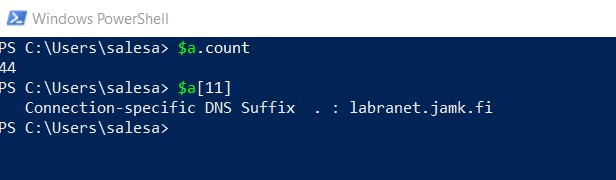
 Now we can get numbers of elements in array, and we can get a specific element of array.
Now we can get numbers of elements in array, and we can get a specific element of array.
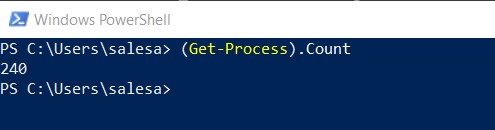
Example: Count how many processes is going on in a computer
(Get-Process).Count
Hashtable
An hashtable can store key-value pairs. So, in and hashtable you do not use a numeric index to address individual elements, but rather the key you assigned to a value.
Creating a New Hash Table
To create a new hash table, use @{}, and specify the key-value pair that is to be stored in your new hash table. Use semi-colons to separate key-value pairs.
# Create a new hash table with key-value pairs
$mydata = @{Name = "PC01"; IP="198.162.10.1"; User="Jack Russell"}
$mydata["IP"]
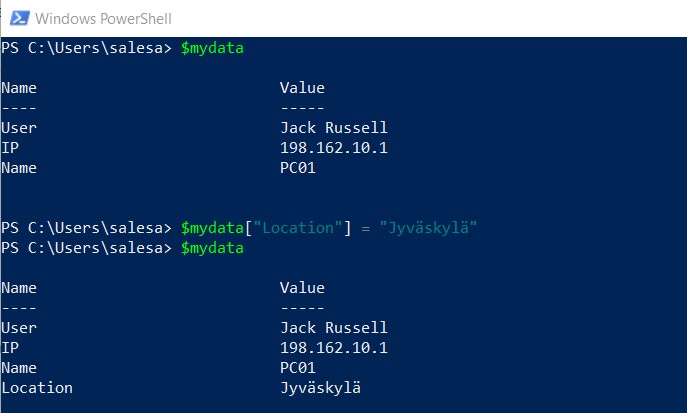
Inserting New Keys in Existing Hash Table
If you'd like to insert new key-value pairs in an existing hash table, just specify the new key and the value that is to be assigned to the new key.
$mydata["Location"] = "Jyväskylä"